- About Us
- Bearings
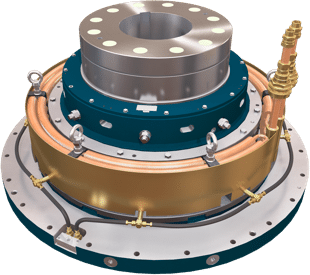 Vertical Bearings
Vertical Bearings
- AV Series
AV
LV SeriesLV
MV SeriesMV
V SeriesV
 Horizontal Bearings
Horizontal Bearings
- HD Series
HD
IH SeriesIH
 Tilting Pad Bearings
Tilting Pad Bearings
 Journal Bearings
Journal Bearings
- Journal Pad Units
Journal
 Thrust Bearings
Thrust Bearings
- SE Series
SE
Omega EqualisedOmega
OmegaOmega
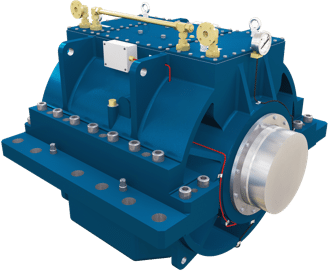 Marine Bearings
Marine Bearings
- Marine Gearbox Internals
Marine
Marine Propulsion Motor
and Generator BearingsEnter your email to download the full paper
"*" indicates required fields
Outline
Home > Advances of Bearing Design for Remote Hydro Power LocationsAdvances of Bearing Design for Remote Hydro Power Locations
J E L Simmons, Michell Bearings, UK
Abstract
Thia paper describes the design and experimental investigation of a new, high speed thrust and journal bearing for hydro power applications. The experimental work covered tests in which the bearing was operated in a self-contained mode using water cooling as well as in a conventional external circulating oil arrangement. A range of test conditions were applied substantially in advance of those available previously for a bearing of this sort and in particular very high machinery overspeeds were simulated sucessfully. This work opens up the possibility of providing substantial hydro installations free from external lubrication systems. The attendant cost reduction and maintenance implications of this are considerable and relevant especially in those more distant locations where human and mechanical services are not readily available.
Introduction
There have been numerous experimental studies published over many years concerning the behaviour of hydrodynamic bearings. In the main these reports have considered radial loading (journal bearings) or axial loading (thrust bearings). In practice, however, the majority of bearing designs are configured to accept a combination of radial and axial loads. It is perhaps unfortunate therefore that this class of combined bearings should be poorly represented in the literature.
This paper covers part of a recent extensive experillental progrnae to investigate the performance of a new, large, high speed thrust and journal bearing which incorporates some innovative features and is designed for a range of demanding industrial applications such as hydro-generators and water turbines. Because of the very considerable horizontal and vertical loads involved and the need to apply these independently a completely new test rig was devised which is described in the paper.
ACCESS FULL PAPERRecommended articles
Naval Thrust Bearings
PTFE Bearing Technology – An Alternative to Whitemetal
Hydrodynamic Bearings Robust Design Ensures Success
PTFE Faced Thrust Bearings: State of the Art Review and Hydro-generator Applications in the UK
Michell Bearings
Waldridge Way,
Simonside East Industrial Park,
South Shields,
NE34 9PZ.Tel: +44 (0) 191 273 0291
Email: sales@michellbearings.com
Email: hrteam@britishengines.com
Email: recruitment@britishengines.com© Michell Bearings.
Registered Office Address: 11 Glasshouse Street, St Peter's, Newcastle upon Tyne. NE6 1BS. Company registered in England and Wales no. 9390648

 PTFE Bearings
PTFE Bearings